When the lights go out, a generator isn't just a convenience; it's a lifeline. It offers peace of mind, keeping essential appliances running and your family comfortable during utility outages. However, effectively and safely hooking up a generator to your house involves more than just plugging in a few extension cords. It requires proper integration into your home's electrical system, a process that prioritizes safety, compliance, and professional expertise above all else.
This isn't a DIY project for the inexperienced. Improper installation can lead to severe injury, fire, carbon monoxide poisoning, or even death, not to mention heavy fines and voided insurance. Our goal here is to give you a comprehensive understanding of the process, guiding you through the essential considerations and pointing you toward the specific expertise you'll need every step of the way.
Understanding Your Power Needs Before You Connect
Before you even think about connecting a generator, you need to understand what you want it to power. This critical first step helps you choose the right generator and the appropriate connection method for your home. Begin by listing all your essential appliances—think lighting circuits, medical equipment, your refrigerator, or even your internet router.
Remember that high-wattage appliances like electric stoves, central air conditioners, and tumble dryers are typically too demanding for most portable generators. For a rough idea, a petrol-driven generator with around 3500W of rated power can usually handle lights, a TV, fans, and a fridge or freezer for a good 12 hours on a single tank. Knowing your wattage requirements is key to making an informed choice. For help with that decision, Here are a few options for generators that might suit your needs.
Prioritizing Safety: Generator Basics Beyond the Hookup
Safety isn't just about the wiring; it starts the moment you place your generator. Carbon monoxide (CO) is a silent, odorless killer, making proper ventilation non-negotiable. Always place your generator at least 10 feet (3 meters) away from your home, ensuring the exhaust is pointed away from all windows, doors, and vents. Never, under any circumstances, run a generator inside your house, an attached garage, or any enclosed space.
Good ventilation is paramount to prevent CO buildup. Inside your home, always use functioning carbon monoxide detectors when a generator is running. Keep children and pets away from the generator during operation, and ensure it's on a level, stable surface. These fundamental safety measures protect everyone under your roof.
Choosing Your Connection Method: Transfer Switch vs. Mechanical Interlock
Connecting a generator to your home's electrical system requires a safe and legal method to prevent "backfeeding" electricity into the utility grid, which can severely injure or kill utility workers. There are two primary, approved methods: a transfer switch and a mechanical interlock. Professional installation is always highly recommended for both, ensuring compliance with local regulations and prioritizing your safety. Always contact your local Department of Labor and Industries, Planning Department, or Power Company to understand specific requirements and permits in your area.
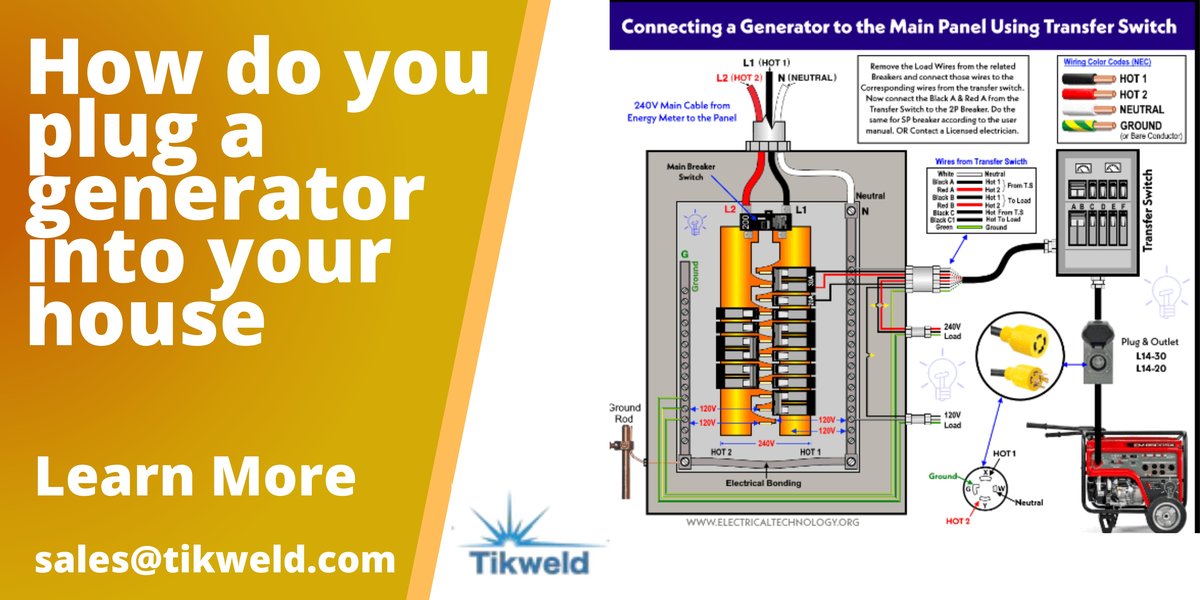
The Transfer Switch: The Safest & Most Recommended Option
A transfer switch is installed between your electrical panel and an exterior power inlet box. It's the gold standard for generator connections, offering unparalleled safety and convenience. This device allows you to safely switch your home's power source from the utility grid to your generator, ensuring the two can never be active simultaneously.
- Preselected Circuits: Transfer switches often come with preselected circuits, meaning you choose beforehand which essential circuits your generator will power, preventing accidental overloads.
- Ease of Use: Once installed, they are simple to operate, requiring minimal monitoring.
- Compliance: Generally, transfer switches are the safest, most reliable, and often the only legally guaranteed option in many areas.
- Professional Installation is Key: Due to the complexity and safety implications, a licensed electrician must install a transfer switch. To learn more about this process, our Manual Transfer Switch Installation and guide offers a deeper dive. For those considering a more permanent, hands-off solution, exploring an Automatic generator setup guide might be beneficial, as these systems inherently use a sophisticated transfer mechanism.
The Mechanical Interlock: A Flexible Alternative (with caveats)
A mechanical interlock is a device installed directly within your electrical panel. It physically prevents both the utility main breaker and the generator main breaker from being turned on simultaneously, accomplishing a similar safety goal as a transfer switch but through a mechanical rather than electrical means.
- Flexible Circuit Selection: Unlike some transfer switches, an interlock allows you to select any circuit in your panel to power, offering greater flexibility.
- Higher Overload Risk: This flexibility comes with a caveat; you must manually monitor your load carefully to avoid overloading your generator.
- Cost and Installation: Mechanical interlocks are generally lower cost and simpler to install if your breaker box has the necessary space and you use a kit approved for your specific panel by the same manufacturer. However, they may be illegal in many areas and can be unsafe if not installed with utmost care and correctness by a professional.
Exploring Direct Connection & Alternative Methods (with serious warnings)
While the appeal of simply plugging your generator into a wall outlet might seem convenient, it's incredibly dangerous and illegal. This practice, known as "backfeeding," can send electricity into the utility grid, risking the lives of utility workers and potentially damaging your home's electrical system. Never plug a generator directly into a wall outlet, your home's wiring, or a washing machine/dryer outlet. For a comprehensive overview of why certain connection methods are dangerous and what constitutes a safe alternative, consult our guide on Direct Connection & Alternative Methods.
Essential Equipment for a Safe Home Generator Connection
Beyond the generator itself, several pieces of equipment are absolutely critical for a safe and compliant setup. This includes a power inlet box, the appropriate gauge power cord, and of course, the transfer switch or mechanical interlock mentioned above. A power inlet box, installed on the exterior of your home, provides a secure and weather-protected connection point for your generator's power cord. Bottom-mount inlets are often preferred for better weather protection.
Choosing a location for your inlet box requires careful consideration: it should be easy to reach from your generator's spot (remember that 10-foot minimum!), not obstruct outdoor features, and be relatively close to your electrical panel to simplify wiring. Just like the transfer switch, the installation of an inlet box is not a DIY task. Professional installation is essential for both safety and code compliance. To ensure you have everything you need, check out our resource on Essential Generator Equipment.
The Professional Installation Process (Focusing on a Transfer Switch)
We cannot stress this enough: a licensed electrician should perform all generator installation work. This ensures your system is safe, up to code, and legally compliant, protecting your home and family. While the steps below provide an overview, they are for informational purposes only and must be carried out by a professional.
- Utility Power Disconnection: The first critical step is to have your local utility company shut off power to your panel and remove the meter. This ensures absolute safety during the electrical work.
- Mounting the Transfer Switch: The electrician will install a mounting board near your main electrical panel and securely attach the transfer switch to it.
- Connecting to the Electrical Panel: Flexible conduit will be run from the transfer switch to your main panel, allowing individual circuits to be safely connected.
- Installing the Power Inlet Box: An appropriate exterior location will be chosen for the power inlet box, and conduit will connect it to the transfer switch.
- System Testing: Before utility power is reconnected, the electrician will thoroughly test the generator and transfer switch to ensure everything operates correctly and safely.
Using Your Generator Safely After Installation
Once your generator system is professionally installed, operating it safely is straightforward but requires adherence to proper procedures.
- Set Up the Generator: Move your generator to its designated outdoor spot, at least 10 feet (3 meters) away from your home, with exhaust clear of all openings.
- Connect the Power Cord: Securely attach the heavy-duty power cord from the exterior power inlet box to your generator.
- Check Oil and Start: Before starting, ensure the engine's oil level is correct; add more if needed, following your user manual. Always unplug and turn off all appliances before operating your generator. Then, follow the manufacturer's instructions to start the engine and allow it to warm up for about five minutes. Never start or stop the generator with electrical devices plugged directly into its outlets.
- Activate Power: Go to your main electrical panel. First, flip off the utility main breaker. Then, turn on the generator main breaker (on your transfer switch or interlock). Finally, slowly flip on the individual circuit breakers you wish to power, one by one. If using a mechanical interlock, continuously monitor the load to avoid exceeding your generator's capacity.
Returning to Utility Power
When grid power is restored, returning to it safely is just as important as starting up.
- Turn Off Circuits: First, flip all individual circuit breakers that were powered by the generator to the "OFF" position, one by one.
- Turn Off Generator Power: Next, turn off the generator main breaker on your transfer switch or interlock.
- Shut Down Generator: Allow the generator to cool for a few minutes, then turn it off by flipping its switch or key into the proper "OFF" position. Always turn off and unplug any appliances your generator is powering before turning off the generator itself.
- Restore Utility Power: Finally, flip your utility main breaker back to the "ON" position.
Maintaining Your Generator for Emergency Readiness
Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure your generator is ready when you need it most. Perform oil changes and check/replace air filters as recommended by the manufacturer. Test your generator monthly by running it under a light load for 20-30 minutes to ensure it starts and runs properly. During these checks, inspect all connections between the generator, power inlet box, and transfer switch. Don't forget to inspect and clean the spark plugs, and keep spare parts like oil filters, spark plugs, and fuel stabilizer on hand.
The Bottom Line: Professional Help is Non-Negotiable
Hooking up a generator to your house safely is a critical project that safeguards your home and family. Improperly installed generators carry immense risks—fire, carbon monoxide poisoning, severe injury, or even death. Electrical work is inherently hazardous and demands professional expertise. Always contact a licensed electrician for installation and inspection to ensure your system meets all safety standards and local codes. This protects not only you but also utility workers and your community. Do not risk your life or the lives of others by attempting an unsafe installation. Have your setup professionally inspected, especially if you lack electrical experience, to ensure safety and valid insurance claims.
Being prepared for power outages doesn't have to be a source of anxiety. With the right knowledge and the invaluable help of qualified professionals, you can confidently power your home, knowing your family is safe and sound.